Friday, October 02, 2020 by Evangelyn Rodriguez
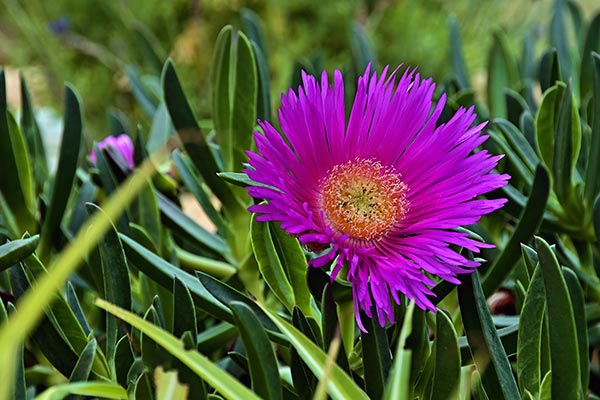
Researchers at the University of Nairobi and the University of Zimbabwe screened the aqueous leaf extract of Carpobrotus edulis (Hottentot fig), a medicinal plant native to Zimbabwe, to determine its phytochemical composition and its effect on hematological parameters. They reported their findings in an article published in The Journal of Phytopharmacology.
- C. edulis leaves are used in folk medicine to treat a variety of ailments.
- To analyze its chemical composition and safety, the researchers obtained aqueous extracts from C. edulis leaves for screening.
- They then divided 32 rats into three treatment groups and one negative control group.
- Group A received 100 mg of the extract per kilogram body weight (mg/kg) while group B received 300 mg/kg and group C received 1,000 mg/kg for 28 days by oral gavage.
- After the 28-day treatment, the researchers measured hematological parameters, such as total red blood cell count (RBC), RBC distribution width, total white blood cell count, hematocrit, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), MCH concentration, platelet counts and mean platelet volume.
- They reported that C. edulis aqueous leaf extracts contained plenty of phytochemicals, such as flavonoids, anthraquinones, alkaloids, terpenoids, saponins, tannins and glycosides.
- The extracts did not exert any adverse effects on the rats or induce abnormal changes in hematological parameters after 28 days of administration.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that C. edulis has no deleterious effects on blood parameters, but they recommend further evaluation of the plant to fully determine its safety for use as medicine.
Read the full study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Mudimba TN, Maitho T, Mbaria J, Taderera T. HEMATOTOXICITY ASSESSMENT OF PHYTOCHEMICALS FROM AQUEOUS LEAF EXTRACTS OF CARPOBROTUS EDULIS. The Journal of Phytopharmacology. 2019;8(4):173-156.