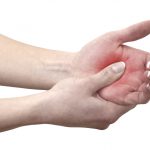
Traditional folk medicine from Pakistan studied to have great anti-inflammatory potential
Tuesday, January 29, 2019 by Ralph Flores
http://www.naturalnewsherbs.com/2019-01-29-traditional-folk-medicine-from-pakistan-studied-to-have-great-anti-inflammatory-potential.html

Many people are quick to dismiss the benefits of folk medicine – with some even going as far as saying it is inferior to modern conventional medicine. However, many treatments in folk medicine have been proven by studies to be effective, despite the opinions of the peanut gallery. A study in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, in particular, suggests that medicinal plants used in traditional folk medicine in Pakistan contain strong antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
The team focused their efforts on plants that have been used in communities in South Punjab in Pakistan, which have been used to address a range of conditions, from skin infections to poisonous bites, as well as other infectious diseases. In the study, the following plants were included:
- Birthwort (Aristolochia indica L.) – The leaves are used to treat poisonous bites and reduce inflammation and itching. It’s also used to address leprosy, stimulate gastric activity, and relieve intermittent fever, diarrhea, and coughing. It can be administered orally or topically.
- Clover dodder (Cuscuta pedicellata) – The stem can either be ingested or applied topically to treat stomachaches and dress wounds and cuts. It’s also used as a laxative, as well as a treatment for hypertension and inflammation.
- Yellow melilot (Melilotus indicus L.) – Topical or oral applications of the leaves can be used to treat inflammation and skin irritation. It also has astringent, anti-coagulant, and laxative properties.
- Puncture vine / Devil’s thorn (Tribulus terresteris L.) – Both the leaves and the fruits of the plants are used to treat inflammation. The fruits of the plant are used to treat abdominal distension and other genitourinary problems, while the leaves are used as a diuretic.
The plants were subjected to various tests to determine its bioactive components, as well as its potential health benefits.
Different names for the same benefits
From the tests, researchers found that all of the plants contained bioactive compounds such as phenols, flavonoids, tannins, phlobatannin, and anthraquinone. These ingredients, according to researchers, give the plants their potent antioxidant activity, which was demonstrated in DPPH and hydrogen peroxide assays.
Out of the four plants, researchers noted that clover dodder extract displayed the highest antibacterial activity against pathogens such as Acinetobacter baumannii, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoneae – known as the ESKAPE pathogens because of its high mortality and morbidity rates upon infection. Researchers also took note of the plant extracts’ antifungal activity, which they attributed to their total phenolic content.
“Positive correlations between total phenolics of selected plant extracts and their antibacterial as well as antifungal potential were obtained,” they wrote in their paper.
The plants were also considered safe for human use, as these were noted to be non-toxic for healthy cells. In potential cancer cells and tumors, the fruit extracts of the puncture vine displayed strong anti-cancer and anti-tumor activity. Earlier studies have only concluded birthwort extracts to have moderate cytotoxicity for cancer cells.
The plants, however, showed great potential in attenuating inflammation, with the clover dodder extract exhibiting the highest potential, based on its ability to reduce biomarkers related to the condition. (Related: Herbs to treat inflammation: The 10 most powerful natural medicines that really work.)
From the findings, researchers concluded that while all of the plants that were studied exhibited bioactivity, the clover dodder extract showed strong positive correlations with phenolic content. “This study revealed that…extracts contain a substantial phenolic content, which was suggested to be the major contributor to their antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory and anti-proteinase activities,” they added. This could lead to a number of developments, which range from advanced treatment for inflammation to even a novel mechanism for the prevention of food spoilage.
If you need more proof of the effectiveness of herbal medicine, follow Herbs.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: alternative medicine, anti-inflammatory, Antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, goodhealth, goodmedicine, goodscience, herbal medicine, medicinal plants, natural cures, remedies, traditional medicine