Black Nightshade – sources, health benefits, nutrients, uses and constituents at NaturalPedia.com
Monday, September 11, 2017 by Jhoanna Robinson
http://www.naturalnewsherbs.com/2017-09-11-black-nightshade-sources-health-benefits-nutrients-uses-and-constituents-at-naturalpedia-com.html
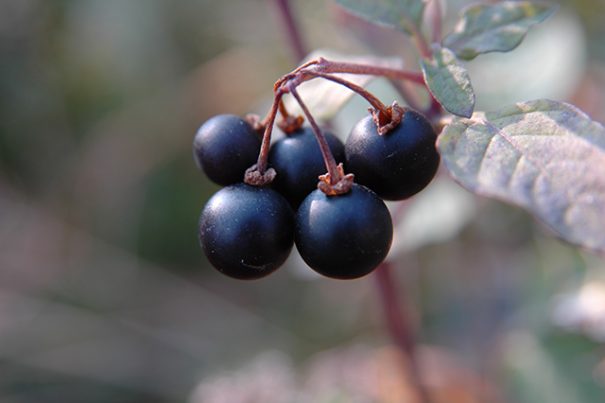

Black nightshade, which has the scientific name Solanum nigrum and which belongs to the family Solanaceae, is a perennial plant that is cultivated in the South of England, also in Northern England, and sometimes Scotland. It is sometimes called garden nightshade.
Black nightshade’s flowers are grouped in clusters at the end of stalks that are attached to the main stems. Its fruits, which usually grow in the late summer to autumn, resemble black berries with a very polished surface, as if they were artificial. Its leaves are soft and thin, arrow-shaped, and can be smooth or hairy in texture depending upon the variety.
Thomas Culpeper, who was a friend of Henry VIII and a relative of both Anna Boleyn and Catherine Howard, said black nightshade should not be confused with the deadly nightshade, and so started calling the former petty morel, noting: “Do not mistake the the deadly nightshade for this, if you know it not, you may then let them both alone.”
Petty morel was used in the 14th century as an addition to wine as a treatment for dropsy, which is an excess of fluid in the cavities or tissues of the body.
Other plant varieties in the Solanaceae family are used for food. For instance, Indian sandalwood (Santalum album) and the Ethiopian eggplant (Solanum aethiopicum) are popular in China and Japan. The Peruvians eat pepino (Solana muricatum) and naranjilla (Solanum quitoense) while cocona (Solanum sessiflorum) is a fruit that is considered a delicacy in Brazil.
List of known nutrients
- Calcium
- Phosphorus
- Vitamin A
Medicinal uses for black nightshade
In Bohemia, which is a region in the western Czech Republic, black nightshade is placed in babies’ cradles to induce sleep.
Black nightshade has diaphoretic properties, meaning it can induce sweating, which is good for people who are trying to lose a fever via a rise in body temperature. One or two grains of black nightshade’s leaves boiled in water and the plant can become an instant sudorific. It can also be used to treat coughs.
Black nightshade has anti-inflammatory properties. It can be used to treat burns, ulcers, and gout when applied topically.
Black nightshade has purgative properties. It can be used to get rid of a bad case of ringworm and alleviate earaches.
Black nightshade has hepatoprotective properties. This means it can prevent the onset of diseases that afflict the liver.
Black nightshade has antibacterial and antispasmodic properties.
Body systems supported by black nightshade
Black nightshade can be a pretty effective treatment for cutaneous conditions, which are basically disorders that affect the integumentary system – the organ system that protects the body form damage such as loss of water or abrasion – which include the skin, hair, and nails.
Black nightshade is good for the cardiovascular system. It has long been considered a cardiac tonic.
Black nightshade is good for the digestive system. It acts as a natural laxative, thus inducing regular bowel movement.
Ways to use black nightshade
Black nightshade can be used as a mouthwash. Just boil the leaves and gargle the leave’s juices and you can find your breath smelling minty fresh after. Its berries can be cooked or eaten out of hand. Its leaves are also edible, and can be eaten as a vegetable or added to stews or soups. It is estimated that over two billion people in the world eat black nightshade and incorporate it into their daily diets.
For black nightshade berry recipes, visit this website.
Where to learn more
Summary
Black nightshade has anti-inflammatory, purgative, hepatoprotective, antibacterial, and atispasmodic properties.
Black nightshade is good for the integumentary, cardiovascular, and digestive systems.
Black nightshade can induce sleep.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: black nightshade