Fu Ling – sources, health benefits, nutrients, uses and constituents at NaturalPedia.com
Tuesday, August 29, 2017 by Frances Bloomfield
http://www.naturalnewsherbs.com/2017-08-29-fu-ling-sources-health-benefits-nutrients-uses-and-constituents-at-naturalpedia-com.html
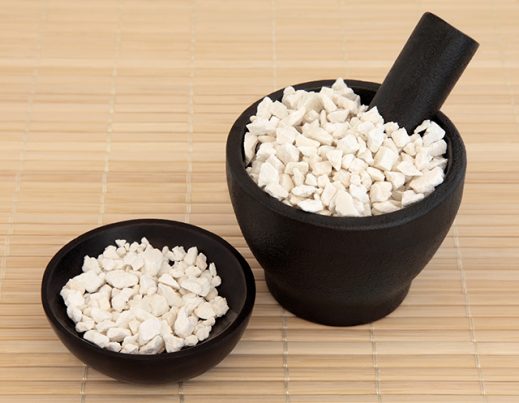

Fu Ling (Poria cocos), also known as poria or China root, is a wood-decaying fungus that grows on the root of pine trees. The filaments — threadlike cells that form the body — of this sweet potato-shaped fungus were harvested for their purported medicinal qualities. The potency of these filaments as remedies were such that they’re valued in traditional Chinese, Japanese, and Korean medicine. Fu Ling continues to be used as a treatment for all kinds of conditions to this day, and the demand for this powerful herb has only grown.

List of known nutrients
There are numerous beneficial constituents present in Fu Ling, most notably:
- Adenine
- Alenine
- Chitin
- Ergosterol
- Eubricoic Acid
- Iron
- Lecithin
- Lipase
- Pinicolic Acid
- Polysaccharides
- Potassium
- Protein
- Sterols
- Tetracyclic Triterpenes
- Tumulosic Acid
- Zinc
The sheer variety and volume of nutrients has given Fu Ling a wide array of medicinal qualities that from sedative to antiviral to anti-inflammatory to diuretic.
Medicinal uses for Fu Ling
When used by practitioners of traditional medicine, Fu Ling is often combined with other herbs to treat health ailments such as:
- Acne
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Anxiety
- Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD)
- Constipation
- Diabetes
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- High Cholesterol
- Hot Flashes
- Inflammation
- Insomnia
- Psoriasis
- Tinnitus
A noteworthy use of Fu Ling is for diarrhea, constipation, and other gastrointestinal problems. In traditional Chinese medicine, Fu Ling is often linked to the expulsion of dampness or stagnant fluids from the digestive system. By promoting the discharge of digestive fluids in a safe and gentle manner, Fu Ling helps keep the digestive system healthy and less prone to the aforementioned conditions.
When compared to hormone replacement therapy, Fu Ling has been found to be better at providing relief to the face and upper body. Thus, Fu Ling can aid women struggling with the hot flashes typically associated with menopause.
The anti-inflammatory quality of Fu Ling makes it ideal for treating ailments resulting from inflammation, such as psoriasis.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, Fu Ling has nourishing and moisturizing properties that become even more apparent when topically applied. As a result, Fu Ling is present in numerous Chinese skin treatments for acne and wrinkles, as well as cosmetic products.
Body systems supported by Fu Ling
Fu Ling is believed to be good for:
- Digestive System
- Immune System
- Kidneys
- Liver
- Spleen
Fu Ling can play an important role in boosting the immune system. Firstly through its anti-inflammatory effects; secondly, by strengthening the response of the immune system to foreign pathogens with the aid of its helpful polysaccharides; thirdly, with its anti-viral and anti-bacterial properties, which greatly decrease the potential harmful effects of foreign pathogens.
Fu Ling has diuretic effects that ease the load on the kidneys. Furthermore, it’s said that Fu Ling can strengthen the kidneys and make them more resistant to sickness.
Ways to use Fu Ling
Fu Ling can be purchased at health food stores and specialty herb shops as a capsule, concentrated powder, herbal tea, or as dried slices.
More than just a supplement, Fu Ling can be incorporated into congee, soups, and cakes thanks to its sweet and light flavor.
Empress Dowager Cixi was said to have on filled pancakes made of finely ground Fu Ling to treat her poor appetite and weak health.
Where to learn more
- Heal the root of all disease
- Learn about the Importance of the Classic Chinese Six Flavor Tea Pill
- Lyme Disease: Traditional Chinese Medicine Offers Treatment for the Toxic Fire
- Relieve Dysmenorrhea Pain with Acupuncture
- Treat Insomnia with Chinese Herbal Medicine
Summary
Fu Ling can alleviate the symptoms of diarrhea, hot flashes, psoriasis, and acne.
Moreover, Fu Ling can nourish and support the kidneys, and the digestive and immune system.
Sources include:
Home-Remedies-For-You.com
TraditionalHerb.org
Herbs.LoveToKnow.com
VeryWell.com
Homemade-Chinese-Soups.com
Tagged Under: Tags: Fu Ling