Indian Mustard – sources, health benefits, nutrients, uses and constituents at NaturalPedia.com
Tuesday, August 08, 2017 by Jhoanna Robinson
http://www.naturalnewsherbs.com/2017-08-08-indian-mustard-sources-health-benefits-nutrients-uses-and-constituents-at-naturalpedia-com.html
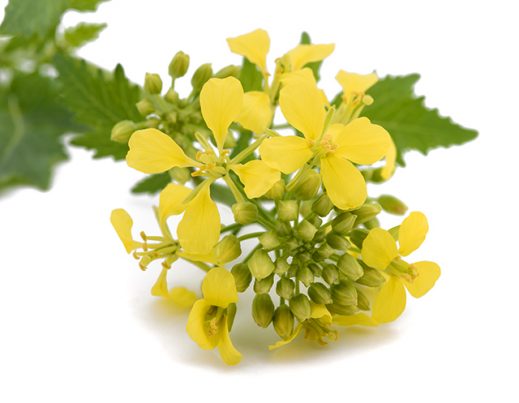

Indian mustard, which is also called mustard greens and has a scientific name of Brassica juncea comes from the Brassica family, which Brussel sprouts, cabbage, and broccoli are also a member of. It is endemic to the Himalayan region of India and have been in use for over 5,000 years. It comes in red, purple, and green, with green being the most common type in the United States.
Indian mustard’s leaves have toothed, scalloped, frilled, or lacey edges. It has golden yellow flowers and acrid-tasting brown seeds.
Indian mustard is classified into many kinds: Chinese green mustard, southern giant curled mustard, Ethiopian mustard, green-in-snow, red giant, French brown, Burgonde tilney, cha tsoi, mizuna, Florida broadleaf, Osaka purple-leaved, and tai tau choi.
List of known nutrients
- Betaine
- Calcium
- Carbohydrates
- Choline
- Copper
- Dietary Fiber
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Protein
- Selenium
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
- Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
- Zinc
Medicinal uses for Indian mustard
Indian mustard is good for regulating cholesterol levels in the body and lowering hypertension. This is because Indian mustard stimulates the process of bile binding, which is also good for lessening the risks of cancer and heart diseases.
Indian mustard is good for purifying the blood. Its high cholorophyll content enables it to neutralize environmental toxins from the bloodstream while at the same time eliminating chemicals, pesticides, and heavy metals in the body.
Indian mustard is good for the skin. Its vitamin C content provides for collagen buildup in the skin, thereby maintaining its health and radiance and preventing the formation of acne.
Indian mustard has anti-inflammation properties. It lessens the painful symptoms of arthritis.
Body systems supported by Indian mustard
Indian mustard is good for the digestive system. The fiber in Indian mustard helps get rid of harmful toxins in the digestive tract. It also protects against risks of having hemorrhoids, colon cancer, and constipation.
Indian mustard is good for the skeletal system. Its vitamin K content – around 524 percent of the recommended daily intake in just one cup – stops bone loss in people with osteoporosis. A word of warning, however: too much consumption of Indian mustard can lead to blood clots. Also, people who are suffering from oxalate urinary tract stones are advised against eating leafy greens from the Brassica family such as Indian mustards, for the natural substances in these vegetables can cause oxalate stones to crystallize, thus aggravating patients’ conditions.
Indian mustard is good for the immune system. A cup of it has nearly 60 percent of the recommended daily value for vitamin C, which acts as an antioxidant that fights off free radicals and repairs cell damage in the body, thus shielding the body against common seasonal ailments like colds and the flu.
Indian mustard also supports the ocular, circulatory, and nervous systems.
Ways to use Indian mustard
Indian mustard is best sauted, along with other vegetables such as kale or spinach, to reduce its slightly peppery taste. You can also try incorporating it into a soup along with other grins to make the soup hearty and flavorful.
Here are some easy-to-prepare Indian mustard dishes for you to enjoy.
Where to learn more
Summary
Indian mustard is good for the digestive, skeletal, immune, ocular, circulatory, and nervous systems.
Indian mustard is good for regulating cholesterol levels in the body and lowering hypertension.
Indian mustard is good for purifying the blood.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: Indian mustard