Annatto – sources, health benefits, nutrients, uses and constituents at NaturalPedia.com
Friday, July 21, 2017 by Frances Bloomfield
http://www.naturalnewsherbs.com/2017-07-21-annatto-sources-health-benefits-nutrients-uses-and-constituents-at-naturalpedia-com.html
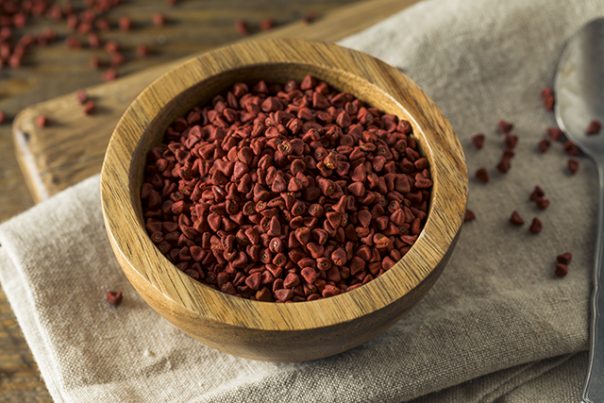

Annatto is a natural food coloring and condiment derived from the seeds of the achiote fruit (Bixa orellana), a tropical shrub native to Central and South America, and the Caribbean. Throughout the centuries, the reddish-orange extract and seeds have been utilized in a variety of medicinal and practical applications. These range from being used as insect repellent by Amazonian tribes to red body paint by native Americans. Nowadays, annatto is being recognized more as a superfood thanks to its unique composition of health-promoting nutrients and compounds.

List of known nutrients
Annatto is known to contain:
- Calcium
- Carotenoids
- Fiber
- Iron
- Norbixin
- Phosphorus
- Saponins
- Tannins
- Tocotrienols
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- Vitamin B9 (Folate)
- Vitamin C
The high carotenoid content is responsible for more than just the distinctive red color of annatto seeds; these carotenoids can serve as antioxidants for the ocular system and prevent degenerative eye diseases.
One other notable nutrient in annatto is norbixin, a powerful antioxidant with an anti-mutagenic effect on healthy cells that have been exposed to free radicals.
Tocotrienols are another type of antioxidant that are noteworthy for their impact on skin health. A topical application of annatto will bring out the most from tocotrienols, as they’ve been shown to reduce blemishes and wrinkles.
Medicinal uses for annatto
Annatto can relieve or remedy the symptoms of such conditions as:
- Cancer
- Cataracts
- Constipation
- Diabetes
- Epilepsy
- Gonorrhea
- Headaches
- Heartburn
- Inflammation
- Jaundice
- Macular degeneration
- Neural tube defects
- Osteoporosis
- Tumors
Whether taken internally and applied externally, annatto has long been used as an herbal treatment for gonorrhea thanks to the inhibitory effect it has on the disease.
In comparison to other plants, annatto has a noticeably high concentration of calcium, thus making it effective in the prevention of osteoporosis.
Annatto has a great amount of folate as well, making it a must-have for pregnant women, since one of the most important roles of folate is to ensure that babies aren’t born with neural tube defects. However, it’s still recommended that limited amounts of annotto be taken, and under trained medical supervision.
Note: annatto can affect blood sugar levels, so diabetics and individuals who will undergo surgery in the near future should avoid it.
Body systems supported by annatto
Taking annatto can be beneficial for:
- Digestive system
- Endocrine system
- Joints
- Kidneys
- Ocular system
- Skeletal system
- Skin
Apart from its ability to lessen the appearance of skin imperfections, annatto is beneficial for minor skin wounds too. Because of the impressive antioxidant volume, annatto can encourage healthy cell and tissue production, leading to reduced skin damage and scarring.
Thanks to its diuretic qualities, annatto can protect and strengthen the kidneys.
Annatto seeds and leaves are known to be high in fiber, making them effective in maintaining a healthy digestive system.
Ways to use annatto
Annatto is already being used in the United States to color foods like butter, cheese, breakfast cereals, and smoked fish. Outside of the United States, annatto features largely in the cuisines of Latin America, Jamaica, the Marianas, and the Philippines. The sweet and slightly nutty flavor has made annatto popular in stews, yellow rice, chili, and adobong pula, a marinated meat dish.
Where to learn more
- Annatto Coloring Could Replace Deadly Sodium Nitrite Used in Processed Meats
- Are You Being Poisoned On a Daily Basis?
- Health Ranger to launch revolutionary, certified organic, non-GMO preparedness food line this Thursday… affiliates welcomed
- Know what you eat before you eat it
- Know what’s In your food (opinion)
Summary
Annatto is particularly noteworthy superfood thanks to its unique nutritional makeup and the presence of unique antioxidants, like norbixin and tocotrienols. Its wide spectrum of nutrients contributes to the reputation of annatto as a good preventive food against cataracts, gonorrhea, osteoporosis, and many others.
Pregnant women should only take annatto under medical supervision, while diabetics and people intending on undergoing surgery should avoid it altogether.
Sources include:
OrganicFacts.net
HealthBenefitsTimes.com
DrHealthBenefits.com
TheAlternativeDaily.com
Livestrong.com
AllRecipes.com
Tagged Under: Tags: Annatto